The MAAP platform is designed to combine data, algorithms, and computational abilities for the processing and sharing of data related to NASA’s GEDI, ESA’s BIOMASS, and NASA/ISRO’s NISAR missions. These missions generate vastly greater amounts of data than previous Earth observation missions. There are unique challenges to processing, storing, and sharing the relevant data due to the high data volume as well as with the data being collected from varied satellites, aircraft, and ground stations with different resolutions, coverages, and processing levels.
Goals of the MAAP
- Establish an Open Science collaboration framework between ESA and NASA to collaboratively share data, science algorithms and compute resources in order to foster and accelerate scientific research conducted by NASA and ESA scientists.
- Create an interoperable, set of shared resources integrated into a virtual collaborative platform in the cloud with special capabilities for seamless and efficient global Team Science activities.
- Provide seamless open-access to airborne, spaceborne and field ESA and NASA data. Make it easier to discover and use relevant data.
- Foster interoperability between cloud-based visualization, development and compute resources in collaborative work-environments.
- Speed up algorithm development and validation. Ability to scale a scientist’s algorithms (Jupyter notebooks or scripts, typically in Python or R) from small regions of interest to global scale on the Data Processing Service.
An overview of the MAAP platform
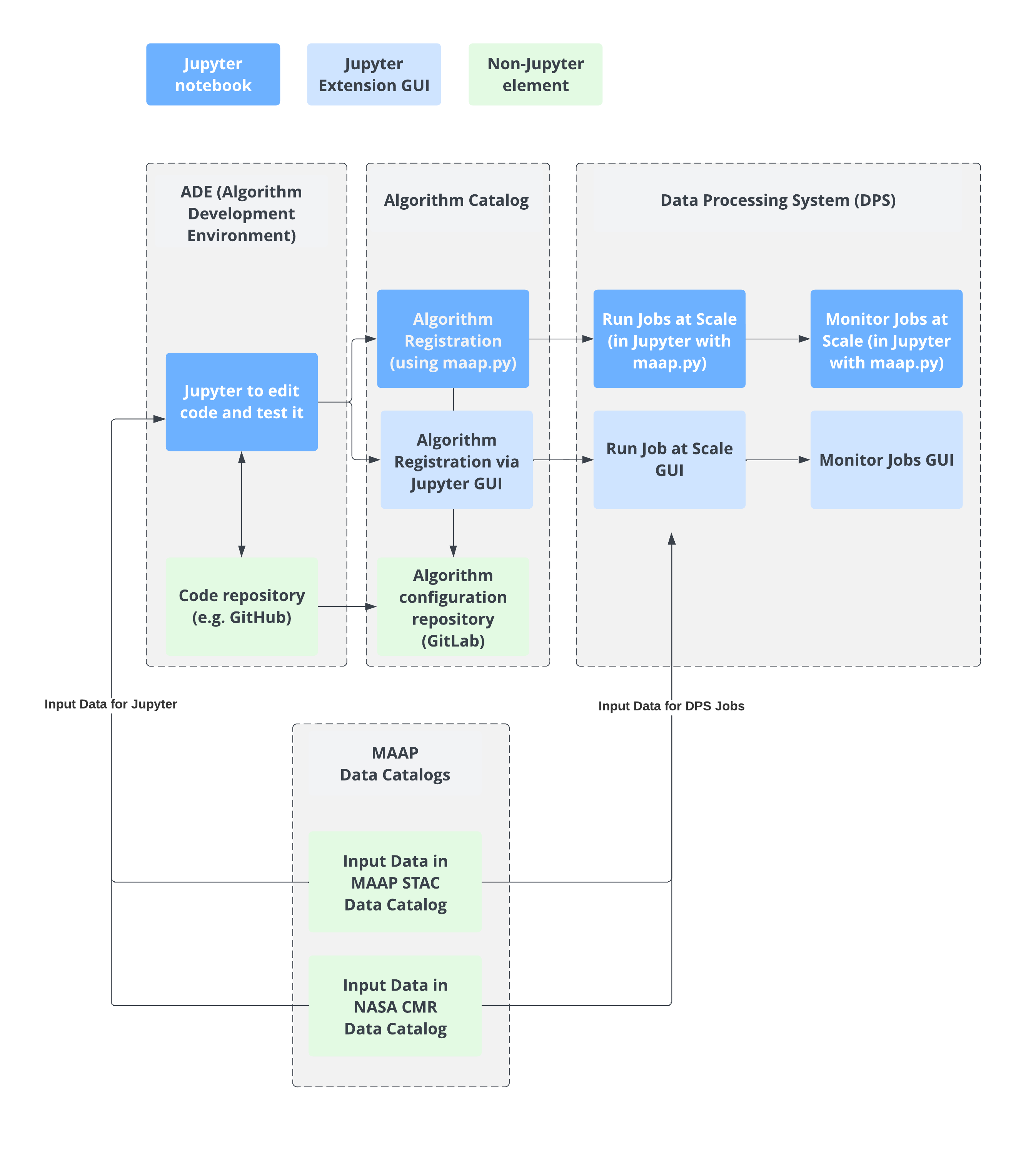
- The Algorithm Development Environment (ADE) is a tool that helps with the development of algorithms in a consistent, standardized environment that helps with the development and testing of algorithms and facilitates large scale data processing. MAAP’s primary user interface is Jupyterlab, where code is written and tested before pushed to the large scale data processing system. Code is stored and checked out from Git-based repositories, including Github and MAAP’s own code repository subsystem.
- The Data Processing System (DPS) is where registered algorithms (see Algorithm Catalog) can be run at scale in the cloud. The MAAP system provides a Jupyter GUI to run Jobs, or the maap.py library can be used to run a batch of Jobs in a loop using Python. The DPS also has monitoring capabilities, and again the MAAP system provides a Jupyter GUI to help monitor Jobs. This can also be done using maap.py in Python.
- The Algorithm Catalog, where your algorithms from the ADE can be registered and compiled for use by the DPS. The MAAP system provides API and GUI tools to help you register and view your algorithms.
- The Code Repository is a git-based repository to store user code. It is also used to store the configuration files necessary for building algorithms to store in the algorithm catalog and for execution in the DPS.
- Input data comes from a few Data Catalogs. Currently there is a MAAP STAC Catalog and the NASA CMR Catalog. More information can be found in the search tutorials section on our documentation site.
